Microsoft Fabric: The Game-Changing Analytics Platform That’s Revolutionizing How Organizations Handle Data
A comprehensive deep-dive into Microsoft’s unified data platform that’s transforming the analytics landscape

Before Microsoft Fabric, creating a simple sales report felt like an impossible task. I still remember CTOs saying “Our data was scattered across seven different systems, each with its own ETL pipelines, security rules, and maintenance headaches. Delivering a single report could take weeks, frustrating both the data team and business stakeholders.” With Fabric, that complexity is finally simplified — bringing everything into one unified platform.
I did three months of hands-on testing, building real solutions, and pushing Fabric to its limits, I’m convinced we’re witnessing something genuinely transformative. Microsoft Fabric isn’t just another analytics tool — it’s a fundamental reimagining of how data platforms should work. And frankly, it’s about time.
The Problem Microsoft Fabric Solves
Let me paint you a picture of what “modern” data architecture looked like. Had Azure Data Factory for data integration, Synapse Analytics for warehousing, Power BI for visualization, Azure ML for machine learning models, and a handful of other specialized tools for real-time analytics. On paper, it looked impressive. In reality? It was a nightmare.
Data engineers spent most of their time playing “data plumber” — moving information from System A to System B, troubleshooting failed connections, and managing different security models across platforms. Meanwhile, data scientists were constantly frustrated because the data they needed was locked away in some other system, requiring weeks of bureaucratic processes to access.
The business users? They’d given up asking for new reports because they knew it meant starting a project that would take months and cost thousands of dollars. Instead, they were back to exporting data to Excel and creating their own “shadow IT” solutions.
This isn’t unique to my experience. According to recent surveys, data teams spend 80% of their time on data engineering tasks and only 20% on actual analysis. That’s not just inefficient — it’s a massive waste of human potential and organizational resources.
What Exactly Is Microsoft Fabric?
Here’s where things get interesting. Microsoft Fabric isn’t just another analytics platform — it’s what happens when someone finally asks, “What if we built this from scratch, knowing everything we know now about data and analytics?”
Think of it as the “iPhone moment” for enterprise analytics. Before the iPhone, we carried separate devices for calls, music, internet, and cameras. Each worked fine individually, but the magic happened when Apple unified everything into a single, integrated experience. That’s exactly what Microsoft has done with Fabric.
Fabric unifies data movement, processing, ingestion, transformation, real-time event routing, and report building into a single Software-as-a-Service experience. But here’s what really caught my attention: it’s built around OneLake — a unified data lake that serves as the single source of truth for all organizational data.
When I first heard about OneLake, I was skeptical. “Another data lake?” I thought. “We’ve seen this before.” But after working with it, I realized this isn’t just another storage solution — it’s a fundamental shift in how we think about data architecture.
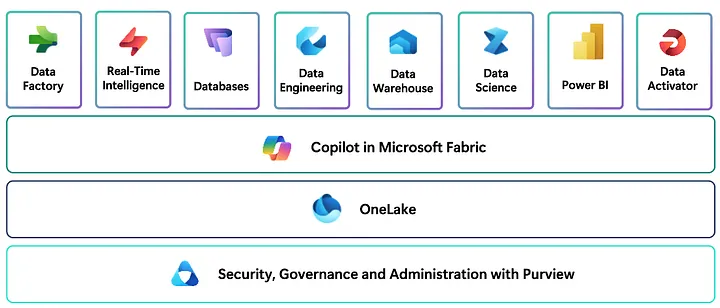
The platform integrates eight core workloads: Data Engineering, Data Factory, Data Science, Data Warehouse, Real-Time Intelligence, Industry Solutions, Databases, and Power BI. Each is tailored for specific user roles while maintaining seamless interoperability. No more data silos. No more complex integrations. No more waiting weeks for data access.
The Eight Pillars of Microsoft Fabric
1. Power BI: Business Intelligence Reimagined
Power BI within Fabric isn’t just your traditional business intelligence tool — it’s been supercharged with AI capabilities and deep integration with the entire Fabric ecosystem. Users can easily connect to any data source within the platform, create stunning visualizations, and share insights across the organization without worrying about data movement or complex ETL processes.
What makes Power BI in Fabric special is its ability to work directly with data in OneLake without requiring data copies or movement. This means reports and dashboards are always working with the most current data, and there’s no need for complex refresh schedules or data synchronization processes.
The integration with Copilot takes this even further, allowing business users to create reports using natural language prompts, generate automated insights, and even create complex DAX calculations without deep technical knowledge. Imagine asking, “Show me sales trends by region for the last quarter with forecasting,” and having a complete dashboard generated automatically.
2. Data Factory: Modern Data Integration
Data Factory in Fabric provides a modern data integration experience that incorporates the simplicity of Power Query with the power of enterprise-grade data movement capabilities. With over 200 native connectors, it can connect to virtually any data source, whether on-premises or in the cloud.
What sets Fabric’s Data Factory apart is its no-code/low-code approach combined with advanced transformation capabilities. Data engineers can design complex ETL/ELT pipelines using visual interfaces, while power users can leverage familiar Power Query experiences for data preparation tasks.
The platform handles everything from simple data copies to complex transformation logic, all while maintaining lineage tracking and governance controls. Real-time monitoring and alerting ensure that data pipelines run smoothly, and automatic retry mechanisms handle transient failures gracefully.
3. Data Engineering: Spark-Powered Analytics
The Data Engineering workload in Fabric provides a comprehensive Apache Spark platform with exceptional authoring experiences. This isn’t just Spark-as-a-Service — it’s a thoughtfully designed environment that makes big data processing accessible to a broader range of users.
Fabric’s Spark integration includes auto-scaling capabilities, optimized performance for common analytics workloads, and seamless integration with other Fabric services. Data engineers can create and manage infrastructures for collecting, storing, processing, and analyzing vast data volumes without worrying about cluster management or resource optimization.
The notebook experience is particularly impressive, offering collaborative development environments with built-in version control, package management, and the ability to schedule notebooks as part of larger data pipelines. The integration with Data Factory allows for sophisticated orchestration scenarios where Spark jobs can be triggered based on data arrival, time schedules, or business events.
4. Real-Time Intelligence: Where the Magic Really Happens
This is where I got genuinely excited about Fabric. Real-Time Intelligence isn’t just about handling streaming data — it’s about creating a living, breathing analytics environment that responds to events as they happen.
I tested this with a simple e-commerce scenario: tracking user behavior on a website in real-time. Within minutes, I had data flowing from web analytics into Eventstreams, being processed and analyzed, and displayed on dashboards that updated in real-time. The entire setup took less time than it used to take just to get approval for a new data source.
The Real-Time Hub serves as mission control for all your streaming data. Whether you’re dealing with IoT sensors, application logs, financial transactions, or social media feeds, everything flows through a unified interface. No more hunting through different systems to find your data streams.
Eventstreams handle the heavy lifting of capturing, transforming, and routing high volumes of real-time events with a no-code experience. I was particularly impressed by the content-based routing capabilities — you can send different types of data to different destinations based on filters, all without writing a single line of code.
But here’s where it gets really interesting: Eventhouses. These are specifically designed for time-based, streaming events with automatic indexing and partitioning. The query performance is genuinely impressive — I was running complex analytics on millions of events with sub-second response times.
5. Data Science: AI/ML at Scale
Fabric’s Data Science workload enables organizations to build, deploy, and operationalize machine learning models seamlessly within the platform. The integration with Azure Machine Learning provides built-in experiment tracking, model registry, and MLOps capabilities.
What makes this particularly powerful is the ability for data scientists to work directly with data in OneLake without needing to move or copy data for model training. This eliminates one of the biggest bottlenecks in traditional ML workflows — data access and preparation.
The platform supports the entire ML lifecycle, from data exploration and feature engineering to model training, validation, and deployment. Automated ML capabilities help democratize machine learning for business analysts, while advanced users have access to the full power of popular frameworks like scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch.
6. Data Warehouse: SQL Performance at Scale
Fabric’s Data Warehouse provides industry-leading SQL performance with the flexibility of separating compute from storage. This architecture allows for independent scaling of both components, optimizing costs while maintaining performance.
The warehouse natively stores data in the open Delta Lake format, ensuring compatibility with other Fabric workloads and external tools. This means data stored in the warehouse is immediately accessible to Spark jobs, Power BI reports, and real-time analytics without any data movement.
Advanced features like automatic indexing, intelligent caching, and query optimization ensure that even complex analytical queries perform exceptionally well. The integration with Copilot provides natural language query capabilities, allowing business users to ask questions in plain English and receive SQL-generated insights.
7. Databases: Operational Data Management
The Databases workload in Fabric provides developer-friendly transactional database capabilities, similar to Azure SQL Database, but with deep integration into the Fabric ecosystem. This allows organizations to build operational applications while maintaining seamless connectivity to their analytical workloads.
The mirroring capability is particularly innovative, allowing organizations to continuously replicate data from various systems directly into OneLake. This includes data from Azure SQL Database, Azure Cosmos DB, Azure Databricks, Snowflake, and other Fabric databases, creating a unified view of operational and analytical data.
8. Industry Solutions: Vertical-Specific Analytics
Fabric provides industry-specific data solutions that address unique sector needs and challenges. These solutions combine data management, analytics, and decision-making capabilities tailored for specific industries like healthcare, financial services, retail, and manufacturing.
These aren’t generic templates — they’re comprehensive solutions that understand industry-specific data models, compliance requirements, and analytical needs. For example, the healthcare solution includes pre-built connectors for FHIR data, compliance frameworks for HIPAA, and analytical models for population health management.
OneLake: The Unifying Foundation
At the heart of Microsoft Fabric lies OneLake — a unified data lake that serves as the foundation for all workloads. Built on Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2, OneLake provides a single, tenant-wide store for all organizational data while maintaining the performance and scale characteristics of modern cloud storage.
OneLake eliminates the need for complex data movement between different systems. When data is ingested into any Fabric workload, it’s automatically stored in OneLake in an open format (Delta Lake) that can be accessed by all other workloads. This means a dataset created by a data engineer can immediately be used by a data scientist for model training, analyzed by a business analyst in Power BI, and processed by real-time analytics — all without any data copying or movement.
The security and governance model of OneLake is particularly sophisticated. Data sensitivity labels and permissions are automatically inherited across all workloads, ensuring consistent security policies regardless of how data is accessed. This eliminates the common problem of having different security models for different tools in the analytics stack.
Copilot in Fabric: The AI Assistant That Actually Works
I’d tried too many “AI-powered” tools that were more marketing than substance. But Copilot in Fabric is different. It’s not just a chatbot slapped onto existing tools; it’s a fundamental reimagining of how we interact with data.
Let me share a real example. Last week, I read a post where on how creating a complex sales analysis that would normally take hours of SQL writing and data modeling. Instead, saying to Copilot: “Show me sales trends by region for the last quarter, include forecasting for the next quarter, and highlight any anomalies.” Within minutes, a complete dashboard with insights.
How Copilot Transforms Each Workload
Data Engineering and Data Science: The code completion here is genuinely impressive. Copilot understands the context of your work and provides suggestions that actually make sense. When I was working on a data transformation pipeline, it suggested optimized Spark code based on my data schema. More importantly, it explained why certain approaches would be more efficient.
Data Factory: This is where Copilot really shines for citizen data developers. I watched a business analyst with no coding experience create a complex data integration pipeline using natural language instructions. The AI generated the transformation logic and even explained what each step was doing.
Data Warehouse: The natural language to SQL capability is a game-changer. Business users can ask questions in plain English and get properly formatted SQL queries. But here’s the clever part — Copilot also explains the query logic, helping users learn SQL concepts along the way.
Power BI: Report creation has never been this intuitive. Describe what you want to see, and Copilot generates not just the visualizations, but also suggests additional insights based on your data patterns.
Real-Time Intelligence: Converting natural language questions into KQL queries makes real-time analytics accessible to users who would never have learned Kusto Query Language otherwise.
Data Agents: The Future of Conversational Analytics
Here’s where things get really futuristic. Data Agents in Microsoft Fabric represent the next evolution of self-service analytics — imagine having a data expert available 24/7 who knows your entire data landscape and can answer any question in plain English.
Now you can set up a Data Agent for your sales team, so instead of submitting requests to the IT team and waiting weeks for reports, sales managers can now ask questions like “Which products are underperforming in the Northeast region?” or “Show me customer churn patterns for enterprise accounts” and get immediate, accurate answers.
How Data Agents Actually Work
Data Agents use Azure OpenAI Assistant APIs to process questions while maintaining strict security protocols. The system evaluates questions against all available data sources — relational databases, Power BI datasets, KQL databases — and determines the most relevant source for each query.
What impressed me most is how the agents handle the translation layer:
•Natural language to SQL for relational databases
•Natural language to DAX for Power BI datasets
•Natural language to KQL for KQL databases
The agent validates queries, executes them, and formats results into human-readable responses. But here’s the clever part — you can configure agents with up to five data sources and add custom instructions that reflect your organization’s specific terminology and business rules.
Real-World Impact
I’ve seen Data Agents transform how different teams interact with data:
Sales Teams: “What’s our pipeline value for Q4?” gets answered instantly instead of requiring a week-long report request.
Operations: “Which suppliers have the highest defect rates?” provides immediate insights for quality management decisions.
Finance: “Show me budget variance by department” delivers real-time financial analysis without waiting for month-end reports.
The democratization effect is profound. People who never would have learned SQL or DAX are now getting sophisticated insights from their data. It’s not replacing data analysts — it’s freeing them up to work on more strategic problems while empowering business users to be self-sufficient.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Manufacturing: Predictive Maintenance and Quality Control
A global manufacturing company implemented Microsoft Fabric to unify data from hundreds of production lines across multiple facilities. Using Real-Time Intelligence, they stream sensor data from machinery into Eventstreams, which automatically detect anomalies and predict maintenance needs.
The Data Science workload processes historical maintenance records and sensor data to build predictive models that can forecast equipment failures weeks in advance. These insights are visualized in Power BI dashboards that maintenance teams access on mobile devices, allowing them to schedule preventive maintenance during planned downtime.
Data Agents allow plant managers to ask questions like “Which machines are most likely to fail in the next month?” and receive detailed insights without needing to understand the underlying ML models or data structures.
Financial Services: Real-Time Fraud Detection
A major bank uses Fabric’s Real-Time Intelligence to process millions of transactions per day, detecting fraudulent activities in near real-time. Transaction data flows through Eventstreams, where complex event processing rules identify suspicious patterns and trigger immediate alerts.
The Data Warehouse stores historical transaction data in Delta Lake format, allowing the Data Science team to continuously refine fraud detection models using the latest data. Power BI dashboards provide real-time visibility into fraud trends, false positive rates, and model performance metrics.
Compliance teams use Data Agents to generate regulatory reports by asking natural language questions about transaction patterns, suspicious activities, and compliance metrics.
Healthcare: Population Health Analytics
A healthcare network implemented Fabric to analyze population health trends across multiple facilities and patient populations. The platform ingests data from electronic health records, claims systems, and public health databases into OneLake.
Data engineers use Spark notebooks to clean and standardize healthcare data from different sources, while ensuring HIPAA compliance through Fabric’s built-in governance controls. The Data Science workload builds predictive models for patient risk stratification and care management.
Clinicians and administrators use Power BI reports to identify high-risk patient populations, track quality metrics, and optimize resource allocation. Data Agents allow healthcare professionals to ask questions about patient outcomes, treatment effectiveness, and population health trends without needing technical expertise.
The Technical Architecture Deep Dive
Compute Engines and Performance Optimization
Microsoft Fabric leverages multiple compute engines optimized for different workload types. The Spark engine handles large-scale data processing and machine learning workloads, with automatic scaling and optimization for common analytics patterns. The SQL engine provides industry-leading performance for data warehousing scenarios, with intelligent caching and query optimization.
The Real-Time Intelligence engine is specifically designed for streaming analytics, with microsecond-level latency for event processing and automatic partitioning for time-series data. All engines share the same underlying storage layer (OneLake), eliminating data movement and ensuring consistent performance across workloads.
Security and Governance Framework
Fabric’s security model is built around the principle of “security by default.” All data is encrypted at rest and in transit, with automatic key management and rotation. Row-level security, column-level security, and dynamic data masking ensure that users only see data they’re authorized to access.
The integration with Microsoft Purview provides comprehensive data governance capabilities, including automated data discovery, classification, and lineage tracking. Data sensitivity labels are automatically applied and inherited across all workloads, ensuring consistent governance policies.
Integration and Extensibility
While Fabric provides comprehensive analytics capabilities, it’s designed to integrate seamlessly with existing systems and tools. The platform supports standard APIs and protocols, allowing integration with third-party tools and custom applications.
The connector ecosystem includes over 200 native connectors for popular data sources, with the ability to create custom connectors for proprietary systems. The platform also supports standard formats like Parquet, Delta Lake, and JSON, ensuring compatibility with external tools and systems.
Comparing Fabric to Traditional Analytics Stacks
Cost Considerations
Traditional analytics architectures often involve multiple vendor licenses, each with different pricing models and minimum commitments. Organizations typically pay for peak capacity across all tools, even when utilization is low.
Fabric’s consumption-based pricing model allows organizations to pay only for what they use, with automatic scaling based on demand. The unified platform eliminates the need for multiple vendor relationships and reduces the complexity of license management.
Operational Complexity
Managing traditional analytics stacks requires specialized expertise for each tool, complex integration projects, and ongoing maintenance of multiple systems. Data teams spend significant time on infrastructure management rather than analytics.
Fabric’s SaaS model eliminates infrastructure management, provides automatic updates and patches, and offers unified monitoring and alerting across all workloads. This allows data teams to focus on delivering business value rather than managing technology.
Time to Value
Traditional analytics projects often take months or years to deliver value, with significant time spent on integration, data movement, and tool configuration. The complexity of multi-vendor environments creates delays and increases project risk.
Fabric’s integrated approach dramatically reduces time to value, with many analytics scenarios deliverable in days or weeks rather than months. The unified data model and shared security framework eliminate many common integration challenges.
The Future of Analytics with Microsoft Fabric
Emerging Capabilities
Microsoft continues to invest heavily in Fabric, with new capabilities being released regularly. Upcoming features include enhanced AI/ML capabilities, additional industry solutions, and expanded real-time analytics functionality.
The integration with Microsoft’s broader AI ecosystem, including Azure OpenAI Service and Cognitive Services, promises to deliver even more sophisticated analytics capabilities in the future.
Industry Impact
Fabric represents a significant shift toward unified analytics platforms, and its success is likely to influence the broader analytics market. Other vendors are already responding with their own integrated platform offerings, suggesting that the days of best-of-breed analytics stacks may be numbered.
The democratization of analytics through AI-powered interfaces like Copilot and Data Agents is likely to expand the user base for analytics tools, bringing data-driven decision making to a broader range of business users.
Getting Started with Microsoft Fabric
Trial and Evaluation
Microsoft offers a free trial of Fabric that provides access to all workloads and capabilities. The trial includes sample data and guided tutorials that help users understand the platform’s capabilities and potential applications.
Organizations should approach the trial strategically, identifying specific use cases that can demonstrate value and building proof-of-concept solutions that showcase the platform’s benefits.
Implementation Strategy
Successful Fabric implementations typically follow a phased approach, starting with specific use cases that can deliver quick wins and gradually expanding to more complex scenarios. Organizations should focus on areas where the integrated platform provides clear advantages over existing solutions.
Change management and training are critical success factors, as teams need to adapt to new ways of working and thinking about analytics. Organizations should invest in comprehensive training programs and consider bringing in external expertise to accelerate adoption.
Best Practices
Based on early adopter experiences, several best practices have emerged for successful Fabric implementations:
1.Start with data governance: Establish clear data governance policies and security frameworks before beginning large-scale data ingestion.
2.Focus on integration: Identify opportunities where Fabric’s integrated approach provides clear advantages over existing point solutions.
3.Invest in training: Ensure that teams have the skills and knowledge needed to take advantage of the platform’s capabilities.
4.Plan for scale: Design solutions with future growth in mind, taking advantage of Fabric’s auto-scaling capabilities.
5.Leverage AI capabilities: Incorporate Copilot and Data Agents into workflows to maximize productivity and democratize analytics.
Who Should Consider Fabric?
Definitely Consider It If:
•You’re struggling with complex, multi-vendor analytics stacks
•Your data teams spend more time on integration than analysis
•You want to democratize analytics across your organization
•You’re already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem
The Bottom Line
Microsoft Fabric isn’t just another analytics platform — it’s a glimpse into the future of how organizations will work with data. The combination of unified architecture, AI-powered interfaces, and consumption-based pricing creates compelling value for most enterprises.
Is it revolutionary? Yes. Is it perfect? Yes. Will it change how you think about analytics? Absolutely.
The question isn’t whether unified analytics platforms like Fabric will become the norm — they will. The question is whether your organization will be ready to take advantage of the opportunities they provide.
If you’re tired of the complexity, frustrated with the silos, and ready for analytics that actually serves your business rather than the other way around, Microsoft Fabric deserves serious consideration.
The future of analytics is integrated, AI-powered, and accessible to everyone. Microsoft Fabric is showing us what that future looks like — and frankly, it’s pretty exciting.
Want to try Microsoft Fabric yourself? Microsoft offers a free trial that gives you access to all workloads and capabilities. I’d recommend starting with a simple use case and gradually exploring the platform’s capabilities. Trust me, once you experience the seamless integration and AI-powered features, you’ll understand why I’m so enthusiastic about this platform.